JavB,
Cita:
|
Empezado por JavB
...Se ha realizado una DLL que accede a un dispositivo físico...A esta DLL le pueden llamar varios programas...El problema es gestionar que los datos que abre o modifica una aplicación sean las mismas para la segunda, tercera etc...Compartir datos en DLL llamada...
|

Revisa esta información:
Cita:
Sharing DLL Data Across Different Processes
Back in the world of 16-bit Windows, DLL memory was handled differently than it is in the 32-bit world of Win32. One often-used trait of 16-bit DLLs is that they share global memory among different applications. In other words, if you declare a global variable in a 16-bit DLL, any application that uses that DLL will have access to that variable, and changes made to that variable by an application will be seen by other applications.
In Win32, this sharing of DLL global data no longer exists. Because each application process maps the DLL to its own address space, the DLL’s data also gets mapped to that same address space. This results in each application getting its own instance of DLL data. Changes made to the DLL global data by one application won’t be seen from another application.
you can still provide a means for applications to share data in a DLL with other applications. The process isn’t automatic, and it requires the use of Memory-Mapped Files to store the shared data.
Memory-mapped files can be used to provide the ability to share data among different processes running on the same machine.
Tomado del libro : Delphi 5 Developer’s Guide (Chapter 9 Dynamic Link Libraries y Chapter 12 Working with Files) de Xavier Pacheco y Steve Teixeira.
|
Revisa este código:
Código Delphi
[-]
library GlobalDataLib;
uses
Windows, SysUtils;
const
FileMapping : PChar = 'GlobalMappingData';
type
PGlobalDllData = ^TGlobalDllData;
TGlobalDllData = record
S1 : String[100];
S2 : String[50];
S3 : Char;
N1 : Integer;
N2 : Double;
N3 : LongWord;
D1 : TDateTime;
A1 : Array[0..9] of Integer;
end;
var
AGlobalData, GlobalData : PGlobalDllData;
MapHandle : THandle;
function GetDLLData : PGlobalDllData; StdCall;
begin
Result := GlobalData;
end;
procedure OpenGlobalData;
var
Size, i : Integer;
begin
Size := SizeOf(TGlobalDllData);
MapHandle := CreateFileMapping(DWord(-1), nil, PAGE_READWRITE, 0, Size, FileMapping);
if MapHandle = 0 then
RaiseLastWin32Error;
GlobalData := MapViewOfFile(MapHandle, FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS, 0, 0, Size);
if GlobalData = nil then
begin
CloseHandle(MapHandle);
RaiseLastWin32Error;
end
else
AGlobalData := GetDLLData;
if AGlobalData^.S1 <> EmptyStr then
GlobalData^.S1 := AGlobalData^.S1
else
GlobalData^.S1 := EmptyStr;
if AGlobalData^.S2 <> EmptyStr then
GlobalData^.S2 := AGlobalData^.S2
else
GlobalData^.S2 := EmptyStr;
if AGlobalData^.S3 <> '' then
GlobalData^.S3 := AGlobalData^.S3
else
GlobalData^.S3 := #0;
if AGlobalData^.N1 <> 0 then
GlobalData^.N1 := AGlobalData^.N1
else
GlobalData^.N1 := 0;
if AGlobalData^.N2 <> 0 then
GlobalData^.N2 := AGlobalData^.N2
else
GlobalData^.N2 := 0;
if AGlobalData^.N3 <> 0 then
GlobalData^.N3 := AGlobalData^.N3
else
GlobalData^.N3 := 0;
if AGlobalData^.D1 <> 0 then
GlobalData^.D1 := AGlobalData^.D1
else
GlobalData^.D1 := 0;
for i := Low(AGlobalData^.A1) to High(AGlobalData^.A1) do
begin
if AGlobalData^.A1[i] <> 0 then
GlobalData^.A1[i] := AGlobalData^.A1[i]
else
GlobalData^.A1[i] := 0;
end;
end;
procedure CloseGlobalData;
begin
UnmapViewOfFile(GlobalData);
CloseHandle(MapHandle);
end;
procedure DLLEntryPoint(dwReason: DWord);
begin
case dwReason of
DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: OpenGlobalData;
DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: CloseGlobalData;
end;
end;
exports
GetDLLData;
begin
DllProc := @DLLEntryPoint;
DLLEntryPoint(DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH);
end.
Código Delphi
[-]
unit Unit1;
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms,
Dialogs, StdCtrls, ExtCtrls, Math;
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
ListBox1: TListBox;
Button1: TButton;
Timer1: TTimer;
procedure Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
procedure Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
private
public
end;
PGlobalDllData = ^TGlobalDllData;
TGlobalDllData = record
S1 : String[100];
S2 : String[50];
S3 : Char;
N1 : Integer;
N2 : Double;
N3 : LongWord;
D1 : TDateTime;
A1 : Array[0..9] of Integer;
end;
function GetDLLData : PGlobalDLLData; stdcall; external 'GlobalDataLib.dll';
var
Form1: TForm1;
AGlobalData : PGlobalDLLData;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
Timer1.Interval := 100;
Randomize;
AGlobalData := GetDLLData;
end;
procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
var
AuxStr : String;
i : Integer;
begin
ListBox1.Clear;
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('S1 = %s',[AGlobalData^.S1]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('S2 = %s',[AGlobalData^.S2]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('S3 = %s',[AGlobalData^.S3]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('N1 = %d',[AGlobalData^.N1]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('N2 = %n',[AGlobalData^.N2]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('N3 = %d',[AGlobalData^.N3]));
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('D1 = %s',[DateTimeToStr(AGlobalData^.D1)]));
for i := Low(AGlobalData^.A1) to High(AGlobalData^.A1) do
AuxStr := AuxStr + IntToStr(AGlobalData^.A1[i]) + ' ';
Delete(AuxStr,Length(AuxStr),1);
ListBox1.Items.Add(Format('A1 = [%s]',[AuxStr]));
end;
procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
i : Integer;
begin
AGlobalData^.S1 := 'String-' + IntToStr(Random(100));
AGlobalData^.S2 := 'String-' + IntToStr(Random(100));
AGlobalData^.S3 := Chr(RandomRange(33,126));
AGlobalData^.N1 := Random(100);
AGlobalData^.N2 := Random(1000);
AGlobalData^.N3 := Random(1000000);
AGlobalData^.D1 := Now + Random(1095);
for i := Low(AGlobalData^.A1) to High(AGlobalData^.A1) do
AGlobalData^.A1[i] := Random(100);
end;
end.
El código anterior en Delphi 7 sobre Windows 7 Professional x32,
implementa una DLL que comparte data entre diferentes procesos por medio de Memory-Mapped Files y un programa que usa la DLL para monitorear y cambiar aleatoriamente la data compartida, como se puede ver en la siguiente imagen:
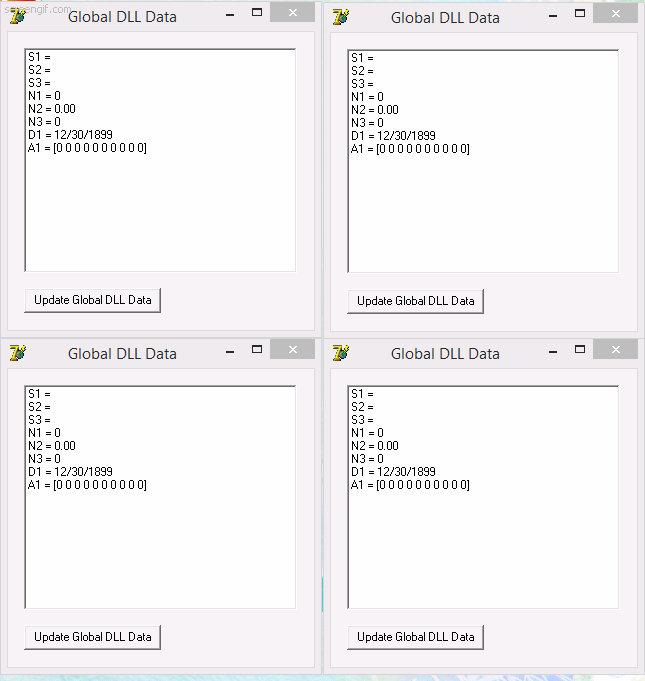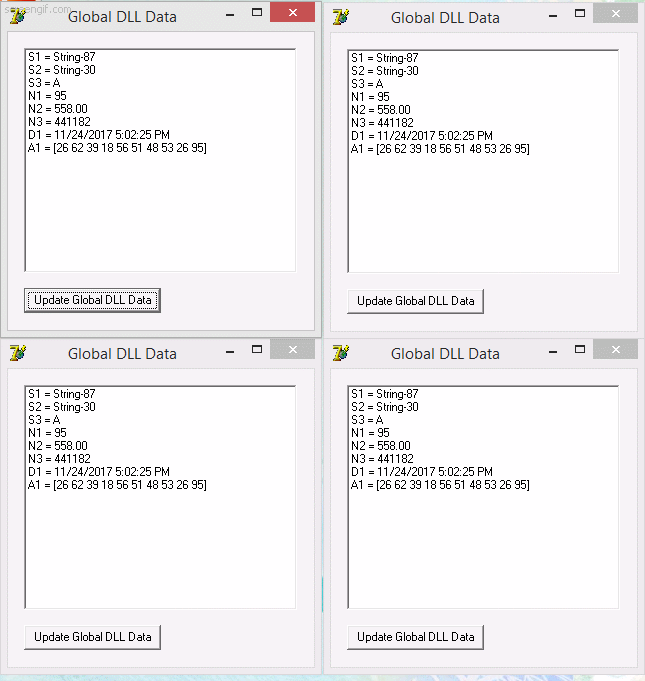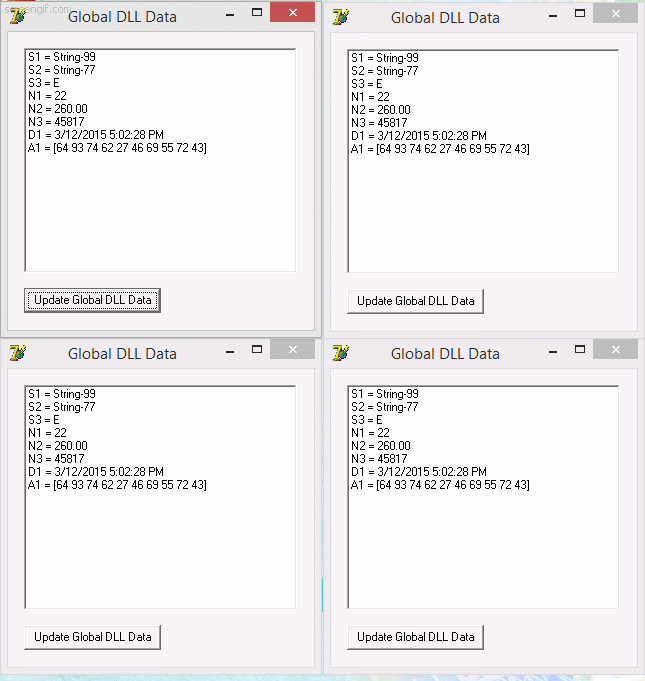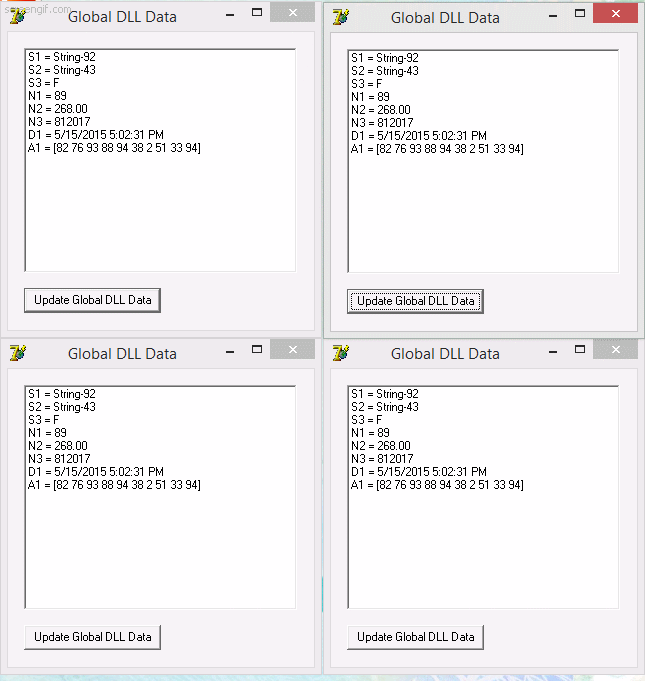
En la imagen se puede ver cuatro programas que usan la DLL GlobalDataLib y comparten la data mapeada en memoria, cualquiera de ellos puede actualizar la data y esta sera vista inmediatamente por los otros programas.
El código del ejemplo esta disponible en : GlobalDataLib.rar
Nota: Con esta técnica se evita el uso de programas Cliente-Servidor, solo en los casos específicos donde pueda aplicarse, pero debe usarse con cuidado dado que todos los programas comparten la misma data que es mapeada en memoria, la clave para los Memory-Mapped Files son las funciones : CreateFileMapping y MapViewOfFile.
Revisa esta información:
Espero sea útil 
Nelson.